Smart Compliance for a Carbon-Regulated Future: Turning Environmental Reporting into Strategic Advantage
Executive Summary
As companies confront supply-chain disruptions, climate extremes and tightening regulations, environmental compliance is evolving from a burden into a strategic asset. This white paper shows how smart compliance – using continuous monitoring (CEMS, IIoT sensors), digital dashboards and automated ESG reporting – can turn mandatory environmental reporting into operational insight and growth. We examine India’s stringent compliance framework (from the Environment Protection Act and Air/Water Acts to new EPR and carbon-trading rules) and the SEBI BRSR ESG-reporting mandate. We demonstrate that organizations investing in real-time data capture not only meet requirements but also gain efficiency, risk resilience and new revenue opportunities.
- Efficient Compliance: Automating data collection with smart monitoring systems eliminates manual errors and lowers costs. For example, continuous sensors can cut operational costs by roughly 10–20% through optimized equipment use.
- Actionable Insights: Integrated ESG dashboards give leadership real-time visibility into energy use, emissions and other metrics. Teams can fix problems or improve processes on the fly, supporting sustainable manufacturing by reducing waste.
- Investor and Market Advantage: Verifiable ESG reporting builds investor confidence. Nearly $34 trillion is expected in ESG-focused assets by 2026, so companies with technology-driven compliance are better positioned for green financing and lower capital costs.

- Efficient Compliance: Automating data collection with smart monitoring systems eliminates manual errors and lowers costs. For example, continuous sensors can cut operational costs by roughly 10–20% through optimized equipment use.
- Actionable Insights: Integrated ESG dashboards give leadership real-time visibility into energy use, emissions and other metrics. Teams can fix problems or improve processes on the fly, supporting sustainable manufacturing by reducing waste.
- Investor and Market Advantage: Verifiable ESG reporting builds investor confidence. Nearly $34 trillion is expected in ESG-focused assets by 2026, so companies with technology-driven compliance are better positioned for green financing and lower capital costs.
Regulation and ESG: From Mandate to Opportunity
Environmental rules no longer just restrict – they drive innovation and resilience. Well-designed policies encourage companies to develop green technologies (Porter Hypothesis). Today, investors, customers and regulators demand transparent ESG reporting. Evidence shows that firms with strong ESG performance have steadier finances and reputations. When these firms deploy technology – real-time EMS (Environmental Monitoring Systems) and IIoT sensor networks feeding cloud dashboards – they align profitability with sustainability. In effect, environmental compliance becomes a core part of enterprise resilience and innovation, rather than just a cost center.

Market Outlook: A Rapidly Expanding Opportunity
The smart environmental monitoring platform market is witnessing remarkable growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns, stricter regulations, and the rise of smart infrastructure. The global market for smart environmental monitoring platforms was valued at USD 5.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 17.1 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.4% from 2025 to 2033.
Key market drivers include the need for regulatory compliance, real-time environmental data, and pollution control across sectors. Urbanization and the emergence of smart cities are accelerating adoption. Smart cities leverage IoT and AI technologies to optimize resources like water, energy, and air quality. This trend is echoed globally, as companies face mounting pressure to align with sustainability goals and stringent ESG mandates. Smart monitoring systems provide real-time insights and compliance assurance, making it critical for future-ready operations.
India’s Environmental and ESG Landscape
India maintains a very comprehensive compliance regime. Key laws include: The Environment (Protection) Act of 1986 (mandating broad pollution standards and annual Form V reporting), the Air Act (1981) and Water Act (1974) (requiring Consent-to-Operate and installation of continuous emission/effluent monitors – CEMS/OCEMS), along with Hazardous Waste (2016) and extended producer responsibility (EPR) rules for e-waste, batteries and plastics. Compliance typically involves obtaining CTE/CTO permits and filing detailed reports on emissions and effluents every year. Plants must install pollution controls – effluent treatment plants, scrubbers, zero-liquid-discharge systems, and CEMS – to meet standards. They also face recycling targets under EPR programs.
Most data submissions are now digital. Companies upload performance data to portals like OCEMS, Parivesh and EPR-PPCB. This transparency improves oversight but demands robust data management. Navigating multiple regulations and lengthy approvals (often reported to take months) is a major challenge, especially for small and mid-size enterprises. In practice, this complexity is increasingly addressed by integrated digital platforms and smart monitoring systems that automatically gather and report required data, reducing delays and risk of non-compliance.
Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA) now mandates real-time monitoring of groundwater quality and levels for projects including saline water extraction. Projects must install piezometers, adopt real time monitoring systems and submit impact assessments, highlighting the growing stringency and digital enforcement in India’s environmental laws.
Smart Monitoring and Digital Compliance
Continuous Environmental Monitoring Systems (CEMS, EQMS, GW Solutions, etc.) and IIoT (Industrial IoT) solutions are the backbone of smart compliance. Instead of relying on periodic manual samples, sensors record emissions, effluent flows, energy use and other parameters round-the-clock. These sensors send data over secure networks to centralized dashboards, where engineers and managers can see real-time plant-wide performance. Deviations trigger instant alerts, enabling proactive fixes (e.g. adjusting a burner, stopping a leak) before non-compliance occurs. Importantly, automated data capture removes human error from reporting – logbooks become obsolete, and even night-shift measurements feed directly into the system with GPS and timestamp verification.
Smart monitoring also supports sustainable manufacturing by optimizing resource use. For instance, IoT-driven energy management systems can throttle equipment during low-demand periods to cut waste. AI analytics forecast material needs and streamline production schedules, reducing scrap and excess inventory. By embedding sensors in machines and utilities, companies can track exactly how much water or electricity is used per unit of product, pinpointing opportunities to improve efficiency. In short, IIoT for industry enables factories to become greener and leaner: studies show that intelligent IoT networks help significantly lower energy consumption and carbon emissions.

Transforming Compliance into Strategic Advantage
Smart compliance yields clear benefits across the business:
- Operational Efficiency & Cost Savings: Automated monitoring cuts waste and labor. By shifting from manual logs to electronic data capture, companies eliminate reporting errors and free up environmental staff for higher-value work. In one example, a plant using smart sensors achieved 100% reporting accuracy and over 30% reduction in unplanned downtime. Across industries, real-time visibility allows precise tuning of processes (like combustion or wastewater treatment) that can reduce energy and material costs by double digits.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: With integrated ESG dashboards, managers see the full picture. Greenhouse-gas emissions, air pollutants, effluent loads and even safety incidents appear on a single screen. This consolidated view empowers faster, evidence-based decisions – from scheduling preventive maintenance to shutting down equipment before an exceedance. Having one “source of truth” for compliance data also strengthens coordination between teams (operations, maintenance, EHS) and drives continuous improvement.
- Capital Access & Differentiation: Transparent, technology-enabled ESG practices attract investors. Lenders and funds increasingly require reliable sustainability data; firms with auditable reports often secure lower financing costs. For example, companies can highlight their certified zero-discharge systems and verified emissions cuts in pitches to banks or equity investors. With global ESG assets approaching $34 trillion, such credibility is a competitive differentiator. It can also unlock new business – like winning bids for green-procurement contracts or qualifying for sustainability-linked loans.
- Regulatory Agility: Regulations are evolving fast. A smart compliance architecture – built on flexible IoT and cloud platforms – adapts without expensive retrofits. New sensor types or reporting fields can be added via software updates. This means companies stay ahead of requirements. Instead of conducting last-minute site audits, they meet evolving rules automatically through their existing systems. In essence, compliance becomes an ongoing capability, not a periodic scramble.
- New Revenue Streams: Beyond avoiding penalties, smart compliance can create value. Continuously logged emission data makes a company ETS-ready. If a plant operates below its carbon intensity target, it earns carbon credit certificates (CCCs) that it can sell to others. Similarly, detailed sustainability scores can be monetized: for example, firms may gain public incentives or tax benefits tied to verified green performance. In short, mastering carbon reporting unlocks the full economic potential of emission reductions.
Emission Trading and Carbon Markets
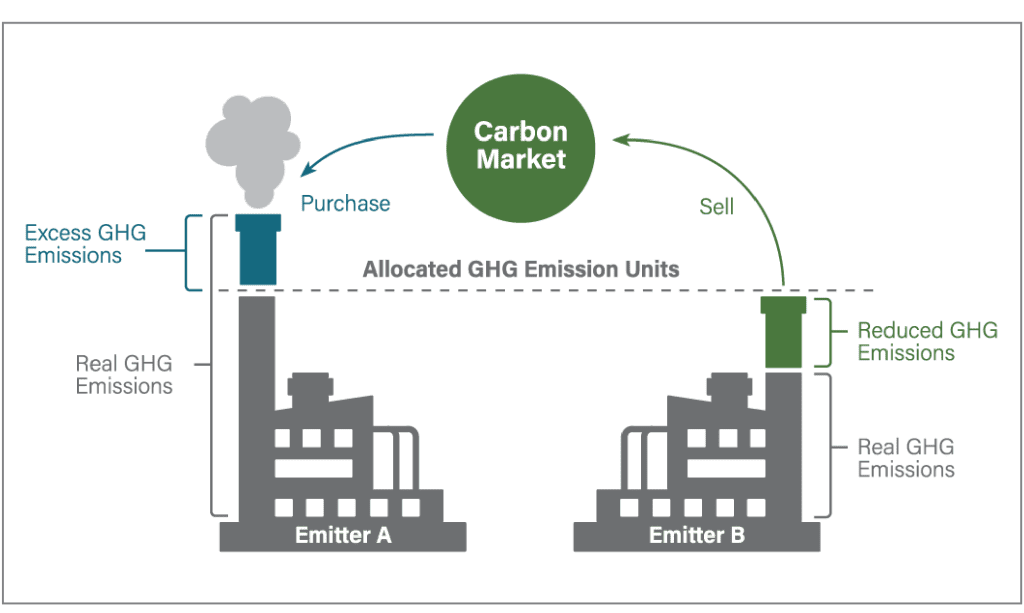
India is moving to put a price on carbon, making smart monitoring even more critical. In 2023 the government finalized rules for the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS) under the amended Energy Conservation Act. This intensity-based system starts in FY2026 and initially covers nine industries (aluminum, cement, fertilizers, steel, petrochemicals, refining, pulp & paper, chloralkali and textiles). Each covered plant will have a mandatory GHG intensity target (e.g. ton CO₂ per ton product). If a plant “overachieves” (emits less than its target), it receives tradeable Carbon Credit Certificates (CCCs). If it falls short, it must surrender or buy extra CCCs.
This cap-and-trade approach builds on India’s existing PAT program. Baselines for the first compliance period will be set using FY2023-24 data. Notably, the CCTS covers both direct and indirect CO₂ emissions for these sectors. In practice, this means plants must demonstrate accurate, verifiable carbon accounts to participate. Smart monitoring is the key: continuous emissions data from CEMS and IoT devices meet the rigorous MRV (measurement, reporting, verification) requirements. Automated systems can flag any parameter deviations instantly, allowing corrections that keep operations “undercap” and generate credits. In other words, an investment in real-time monitoring today directly translates into carbon revenue opportunities tomorrow – aligning compliance with profitability.
Smart Compliance is the Strategic edge
Businesses are being held to higher standards of transparency, performance and accountability. Smart Compliance is how companies can stay ahead. It’s not just about avoiding penalties; it’s about building resilience, gaining real-time insights, and unlocking new value. With automated environmental monitoring, integrated ESG dashboards, and data assurance tools, businesses can move from reactive reporting to proactive leadership.
Firms that invest in Smart Compliance today will be the ones investors trust, partners prefer, and regulators recognize. It’s the foundation for ESG credibility, carbon monetization, and long-term competitive advantage.
In a world where compliance is gaining shareholders’ attention and business sense, early movers will lead.
Case Studies: Smart Monitoring in Action
Axis Solutions Limited (ASL) has implemented smart, real-time monitoring systems across India in power, steel, and infrastructure sectors—enabling clients to go beyond compliance and achieve measurable operational and sustainability gains. Below are some real-life impact projects taken up by Axis Solutions

Remote Water Quality (Jal Jeevan Mission):
Axis Solutions Limited implemented a real-time water monitoring system in remote villages under the Jal Jeevan Mission. Faced with poor GSM connectivity and tough terrain, Axis deployed a LoRa-based IoT network to track water quality parameters. The system enabled 24/7 monitoring, improved water quality assurance and gave local operators real-time insights through a custom cloud dashboard ensuring reliable and compliant water supply in challenging conditions.
Groundwater Compliance (Odisha Steel Plant):
Axis Solutions Limited implemented a real-time groundwater monitoring system for a major steel plant to ensure compliance with CGWA guidelines. The solution included ultrasonic flowmeters, level transmitters, and an IEC 62443-compliant IIoT gateway for secure data transmission to the national hydrology server. A custom dashboard enabled internal monitoring, reducing manual effort and enhancing decision-making. The system delivered full regulatory compliance, improved data accuracy, and was designed to withstand harsh industrial conditions while remaining scalable for future needs.
To meet evolving regulatory demands, only a handful of solution providers offer end-to-end capabilities—from instrumentation to cloud analytics. Axis Solutions stands out by delivering integrated systems that include manufacturing, software, and post-deployment support.
Secure Plant Monitoring (Power Plant, Gujarat):
Axis Solutions Limited deployed a real-time water flow monitoring system for a 656 MW power plant near Surat, Gujarat. With GSM and internet usage restricted, Axis implemented a private LoRaWAN network to transmit data from existing flowmeters to a centralized SCADA dashboard. The system was seamlessly integrated with the plant’s PI server via OPC UA. This solution enabled accurate, real-time monitoring across plant and township utilities, enhanced data security, and improved decision-making—while meeting regulatory needs and completing deployment within just six months.
In each case, clients reported dramatic improvements: 100% data accuracy, much faster responses to issues and roughly 30% less downtime. These metrics underscore how smart environmental monitoring drives both compliance and operational excellence.

Lead the Change
Environmental regulations and ESG requirements are only getting tougher. Smart compliance is now the strategic edge for industry leaders. By embracing smart monitoring systems and IIoT-based monitoring, digital dashboards and automated reporting, companies not only satisfy India’s stringent norms but also boost sustainable manufacturing and corporate resilience. IIoT is revolutionizing industrial sustainability by enabling smarter resource management and reducing waste – and smart compliance is at the heart of that transformation.
Partnering with Axis Solutions Limited (a leader in Industrial IoT and environmental monitoring) can accelerate this journey. From regulatory compliance to carbon credit monetization, we help turn sustainability goals into business results. Get ahead in the carbon-regulated future by making compliance a source of strategic advantage.
Abbreviations and Full Forms
ABBREVIATION | FULL FORM |
CEMS | Continuous Emission Monitoring System |
IIoT | Industrial Internet of Things |
ESG | Environmental, Social, and Governance |
BRSR | Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report |
CGWA | Central Ground Water Authority |
OCEMS | Online Continuous Effluent Monitoring System |
SCADA | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition |
OPC UA | Open Platform Communications – Unified Architecture |
EPR | Extended Producer Responsibility |
ETP | Effluent Treatment Plant |
CTS | Carbon Trading Scheme |
CCCs | Carbon Credit Certificates |
MRV | Measurement, Reporting, and Verification |
PI Server | Plant Information Server (data historian software) |
LoRaWAN | Long Range Wide Area Network |
JJM | Jal Jeevan Mission |
CCR | Central Control Room |
IEC 62443 | International Standard for Industrial Cybersecurity |
PAT | Perform, Achieve and Trade (India’s energy efficiency program) |
GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
ULB | Urban Local Body |
MoEFCC | Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change |
SPCB | State Pollution Control Board |
CPCB | Central Pollution Control Board |
CTE/CTO | Consent to Establish / Consent to Operate |
GRI/TCFD | Global Reporting Initiative / Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures |
References
- CPCB Guidelines for Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS). Central Pollution Control Board, India.
- SEBI BRSR Framework. Securities and Exchange Board of India.
- PwC (2022). Asset and Wealth Management Revolution 2022.
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC). Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- EY India ESG and BRSR Reports (2023).
- Mongabay-India (2023). India’s Carbon Credit Trading Scheme Explained.
- DataTracks. Digital ESG Reporting and Automation Platforms.
- AWS Industrial IoT Architecture. Amazon Web Services.
- Axis Solutions Internal Case Study Presentation, 2024.
- IEA India Energy Outlook Reports.


